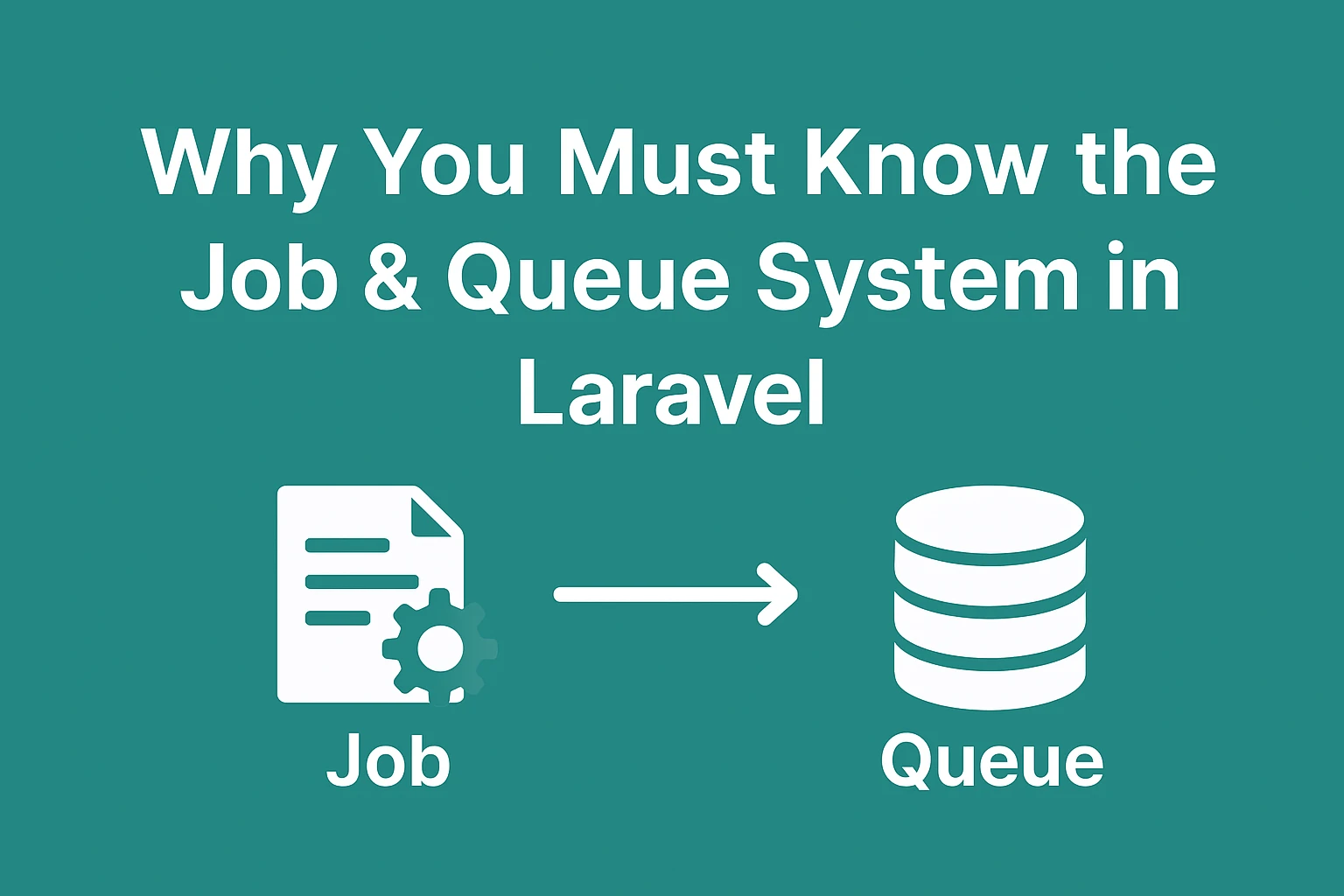
- Job & Queue System in Laravel
- 2 months ago
- 3 min read
If you're building applications with Laravel and still performing every task directly inside the controller — like sending emails, processing files, or making API calls with large responses — you're making your users wait unnecessarily. This not only slows down your application but also frustrates your users.
Laravel provides a Job & Queue System that allows you to handle such tasks in the background — improving both performance and user experience.
🔧 Real-Life Example
Let’s say a user registers on your application. You want to send them a Welcome Email.
❌ The Wrong Way: Doing Everything in the Controller
public function register(Request $request)
{
// Create the user
$user = User::create([
'name' => $request->name,
'email' => $request->email,
'password' => bcrypt($request->password),
]);
// Send welcome email directly — BAD!
Mail::to($user->email)->send(new WelcomeMail($user));
}What happens here?
The user has to wait until the email is fully sent before getting a response. Slow, right?
✅ The Right Way: Use a Queue
Step 1: Create a Job
php artisan make:job SendWelcomeEmailJob
Step 2: Define the Job Logic
use Illuminate\Bus\Queueable;
use Illuminate\Contracts\Queue\ShouldQueue;
use Illuminate\Foundation\Bus\Dispatchable;
use Illuminate\Queue\InteractsWithQueue;
use Illuminate\Queue\SerializesModels;
use App\Mail\WelcomeMail;
use Illuminate\Support\Facades\Mail;
class SendWelcomeEmailJob implements ShouldQueue
{
use Dispatchable, InteractsWithQueue, Queueable, SerializesModels;
protected $user;
public function __construct($user)
{
$this->user = $user;
}
public function handle(): void
{
Mail::to($this->user->email)->send(new WelcomeMail($this->user));
}
}Step 3: Dispatch the Job from the Controller
public function register(Request $request)
{
$user = User::create([
'name' => $request->name,
'email' => $request->email,
'password' => bcrypt($request->password),
]);
// Queue the welcome email to be sent in the background
dispatch(new SendWelcomeEmailJob($user));
return response()->json(['message' => 'Registration successful']);
}🛠️ Set Up the Queue System (Database Driver)
Run the following commands:
php artisan queue:table php artisan migrate
Update your .env file:
QUEUE_CONNECTION=database
Run the queue worker:
php artisan queue:work
✅ What’s the Benefit?
- The user completes registration.
- Gets an instant response within 1 second.
- The welcome email is sent in the background — no delay, no waiting.
⚠️ What Happens If You Don’t Use Jobs & Queues?
- Your user waits too long for a response.
- The server gets overloaded.
- Tasks like email, SMS, and file processing slow everything down.
- Real-time notifications become harder to implement.
- You block the entire user flow with heavy tasks like Mail::send().
✅ With Jobs & Queues:
- Everything runs asynchronously.
- Your server handles more requests smoothly.
- Users stay happy with fast and responsive experiences.
Conclusion:
If you’re building scalable and efficient Laravel applications, learning and using the Job & Queue System is not optional — it’s essential.

A Step-by-Step Guide to Install Laravel
Mastering Laravel Routes A Complete Guide to Efficient Routing
Laravel Route Redirection Simple and Efficient URL Management
Comprehensive Guide to Laravel Frontend Blade Snippets

A Comprehensive Guide to Laravel Form Validation
Mastering Laravel Form Requests
Exploring Laravel's __invoke Controller Method

Unlocking Lightning-Fast Search in Laravel with TNTSearch
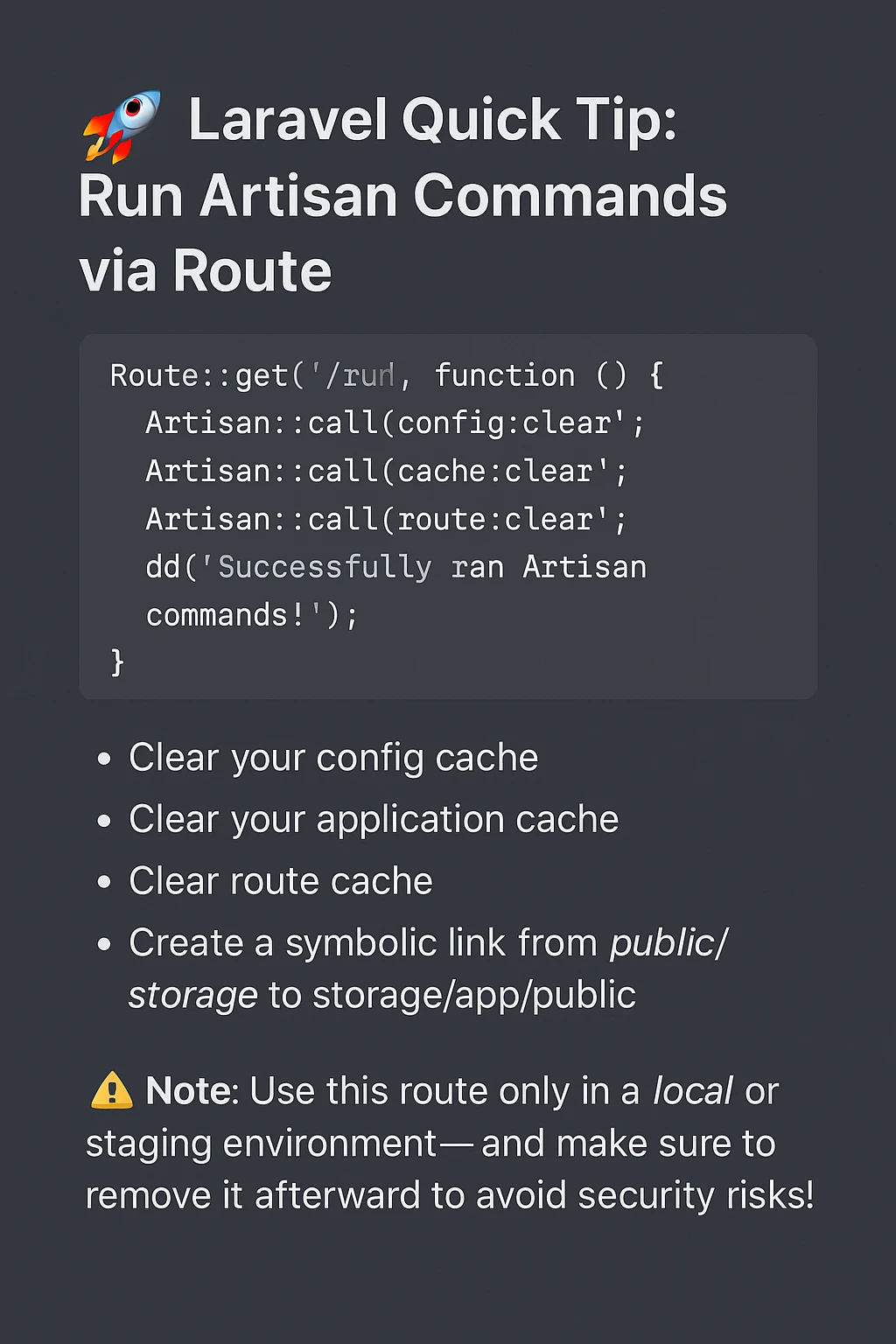
Run Artisan Commands via Route

